organic chemistry - Why does the reduction of naphthalene with nickel/ hydrogen lead to trans-decalin? - Chemistry Stack Exchange
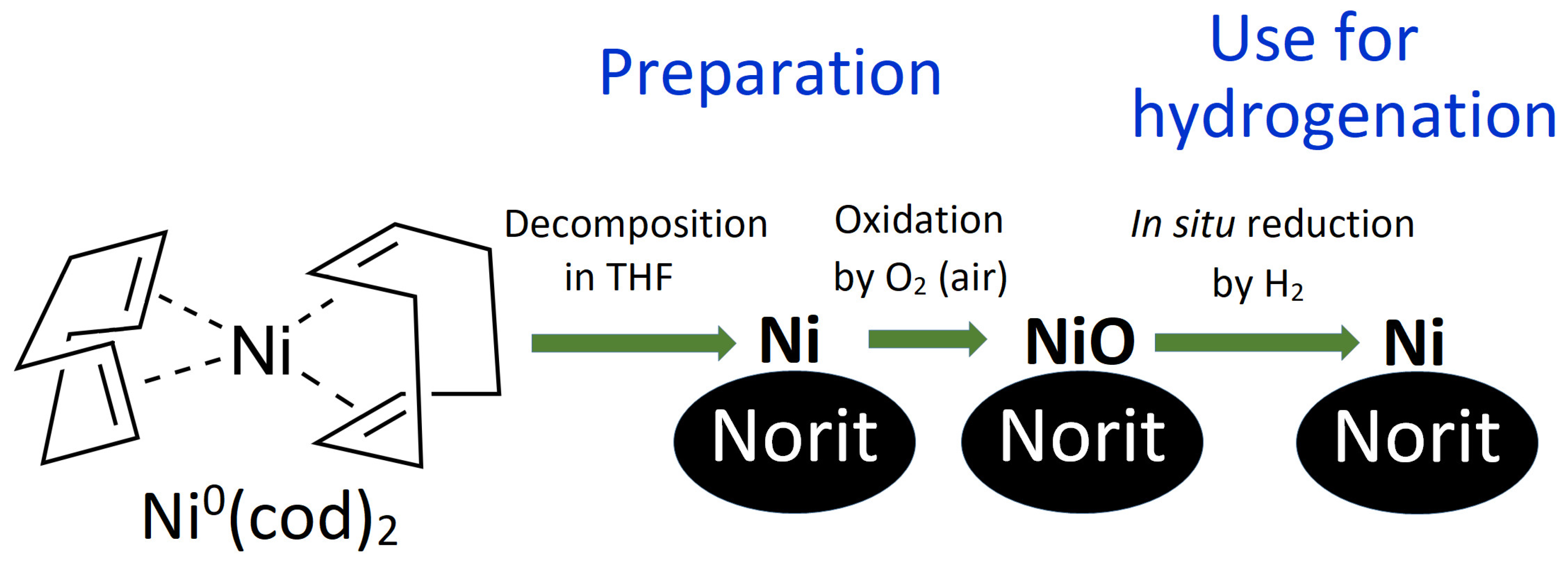
Catalysts | Free Full-Text | Air-Stable Efficient Nickel Catalyst for Hydrogenation of Organic Compounds
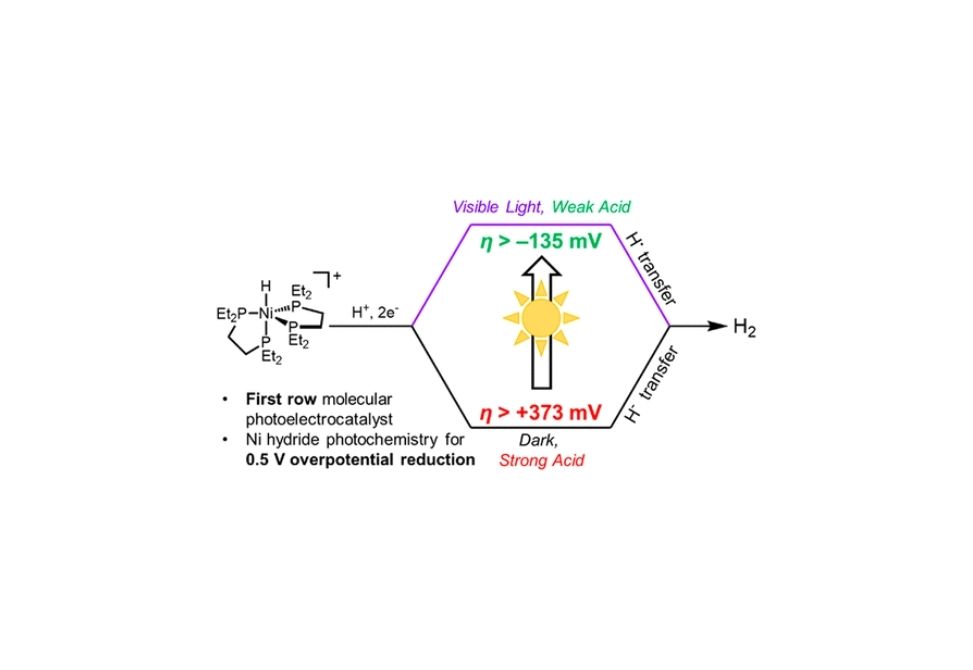
Photochemical H2 Evolution from Bis(diphosphine)nickel Hydrides Enables Low-Overpotential Electrocatalysis – Department of Chemistry
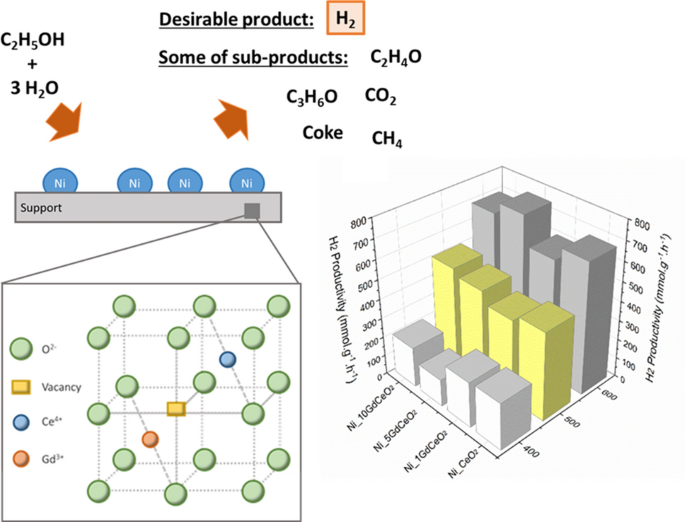
Ethanol Steam Reforming by Ni Catalysts for H2 Production: Evaluation of Gd Effect in CeO2 Support | SpringerLink

Catalytic reduction of benzaldehyde to toluene over Ni/γ-Al2O3 in the presence of aniline and H2 - ScienceDirect

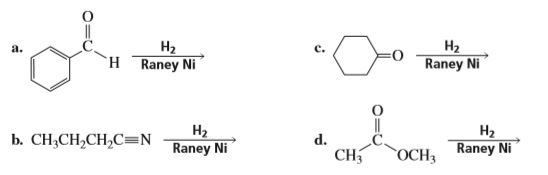
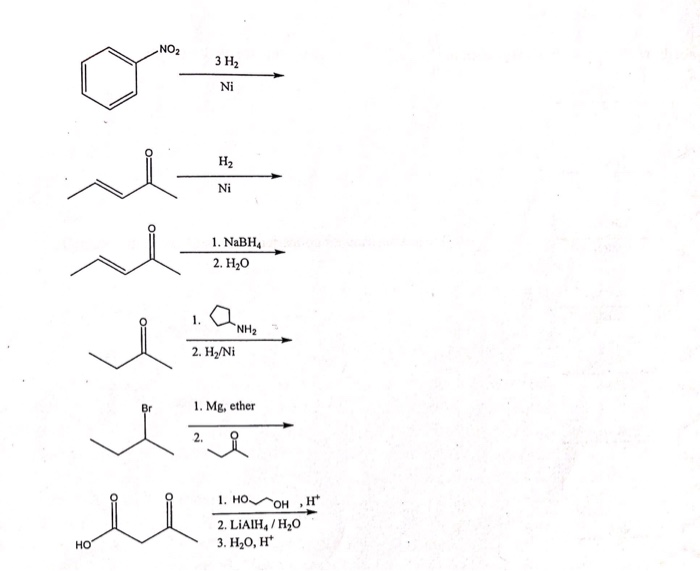
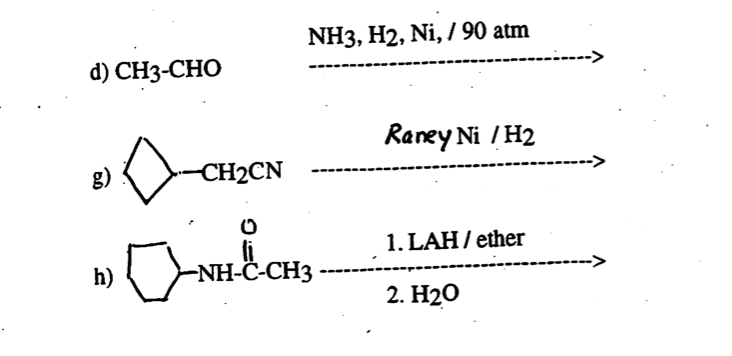
Complete the following reaction: CN H2/Ni a) b) CH3 Br H3PO2 + H2O N2Clo Alcoholic KOH CH2-NH2 + CHCl3

Core–shell NaBH4@Ni Nanoarchitectures: A Platform for Tunable Hydrogen Storage - Salman - 2022 - ChemSusChem - Wiley Online Library

Selective methanation of CO in H2-rich gas stream by synthetic nickel-containing smectite based catalysts - ScienceDirect
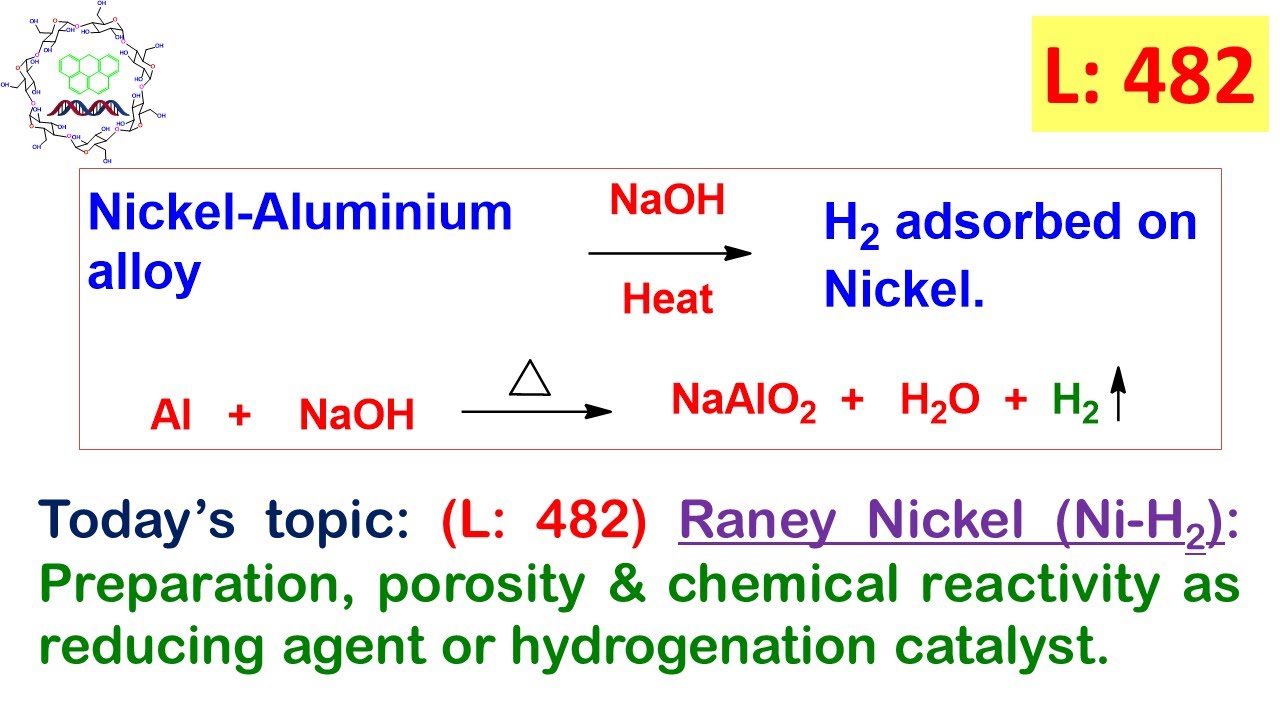
L: 482) Raney Nickel (Ni-H2): Preparation, porosity, reducing agent and hydrogenation catalyst. - YouTube
Which of the following functional groups can not be reduced by H2/Ni R-CHO R-COH R-COO-R R-Co-R? - Quora
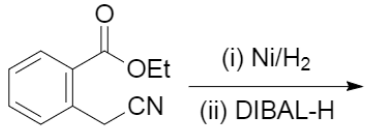
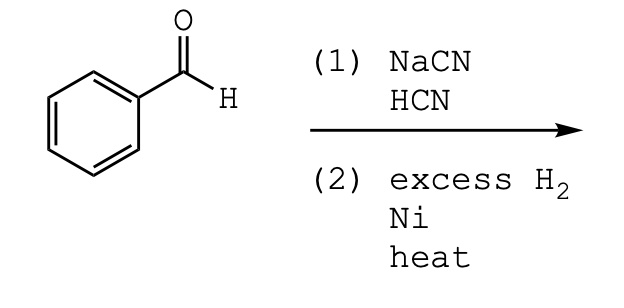

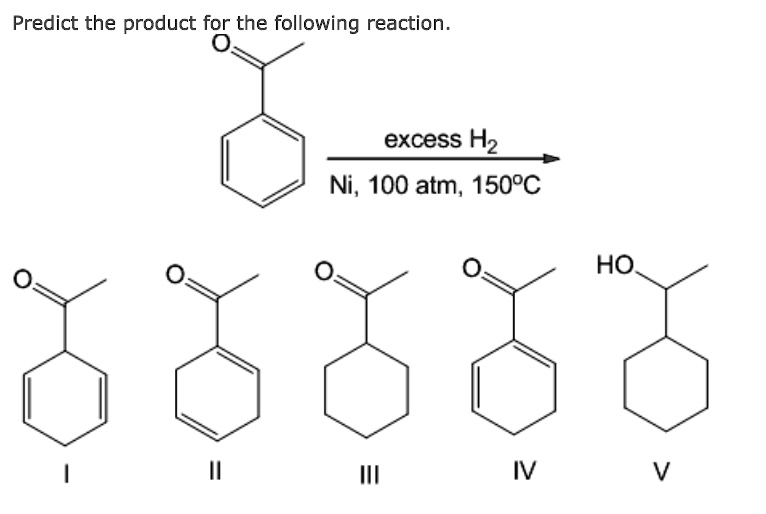
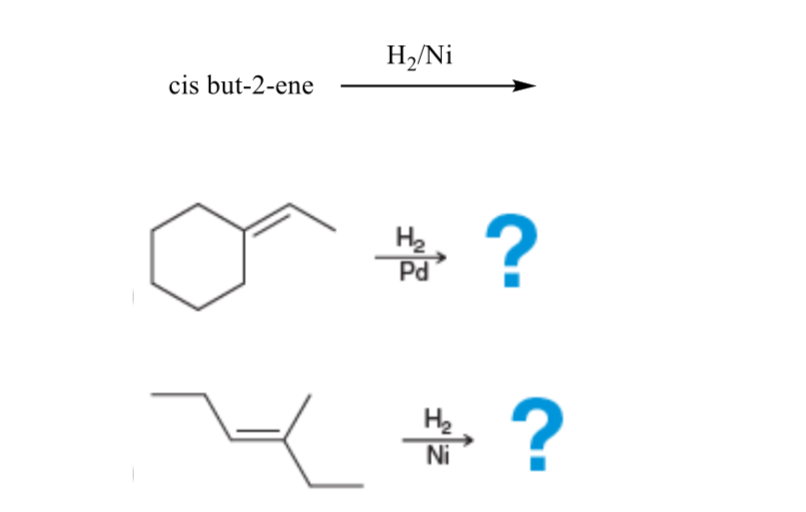
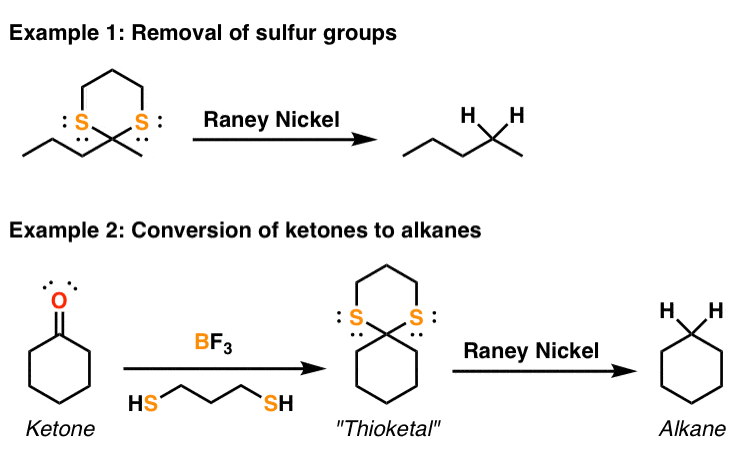
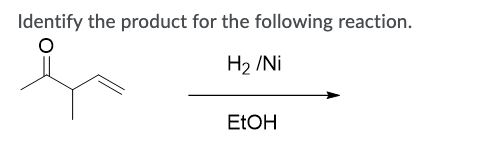

![Reduction of acetophenone using Raney Ni–Al alloy in H2O [96] | Download Scientific Diagram Reduction of acetophenone using Raney Ni–Al alloy in H2O [96] | Download Scientific Diagram](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325304529/figure/fig6/AS:962195290611716@1606416642161/Reduction-of-acetophenone-using-Raney-Ni-Al-alloy-in-H2O-96.gif)